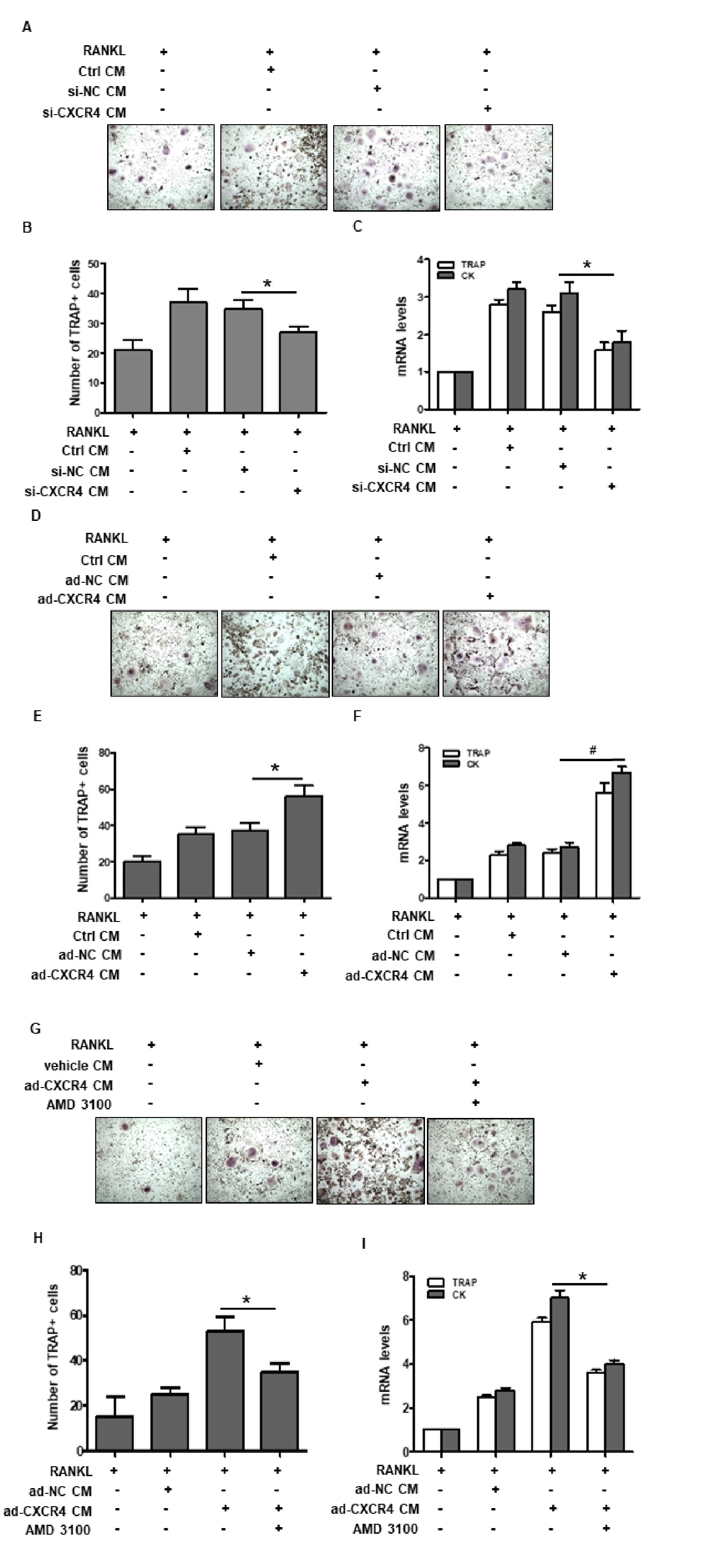
Fig. 5. Effects of CXCR4 manipulation in NSCLC on osteoclast progenitor cell differentiation. A. TRAP staining was performed to evaluate the formation of multinucleated cells. RAW264.7 cells were treated with 10 ng/mL RNAKL with or without H1299 culture medium (CM) harvested from the CXCR4-knockdown group or the control transfection group. B. Quantification of TRAP-positive cells (n=3, *p<0.05 compared with the negative control siRNA group). C. The mRNA levels of the osteoclast differentiation marker genes cathepsin K and TRAP in treated RAW264.7 cells were measured via RT-PCR at 48 h after treatment (n=3, *p<0.05 compared with the negative control siRNA group). D. TRAP staining of osteoclast progenitor cells when CXCR4 was overexpressed. RAW264.7 cells were treated with 10 ng/mL RNAKL with or without H1975 CM harvested from the CXCR4-overexpression group compared with the adenovirus or control group. E. Quantification of TRAP-positive cells upon stimulation with cell culture media from CXCR4-overexpressing H1975 (n=3, *p<0.05 compared with the adenovirus negative control group). F. mRNA levels of the osteoclast differentiation marker genes cathepsin K and TRAP in treated RAW264.7 cells were measured via RT-PCR at 48 h after treatment (n=3, #p<0.01 compared with the negative control adenovirus transfection group). G. TRAP staining was performed to detect RAW264.7 cell differentiation following treatment with 10 ng/mL RNAKL and culture medium from CXCR4-overexpressing H1975 cells in the presence or absence of 10 ng/ml AMD3100, as indicated. H. Quantification of TRAP-positive cells upon stimulation with culture media from CXCR4-overexpressing H1975 cells in the presence or absence of AMD3100 (n=3, *p<0.05). I. mRNA levels of osteoclast differentiation marker genes cathepsin K and TRAP in treated RAW264.7 cells were measured via RT-PCR at 48 h in the indicated groups (n=3, *p<0.05).